Converting Measured Values to Sequence ComponentsPositive, Negative and Zero Sequence Components are often a key aspect of analysis of power system conditions. 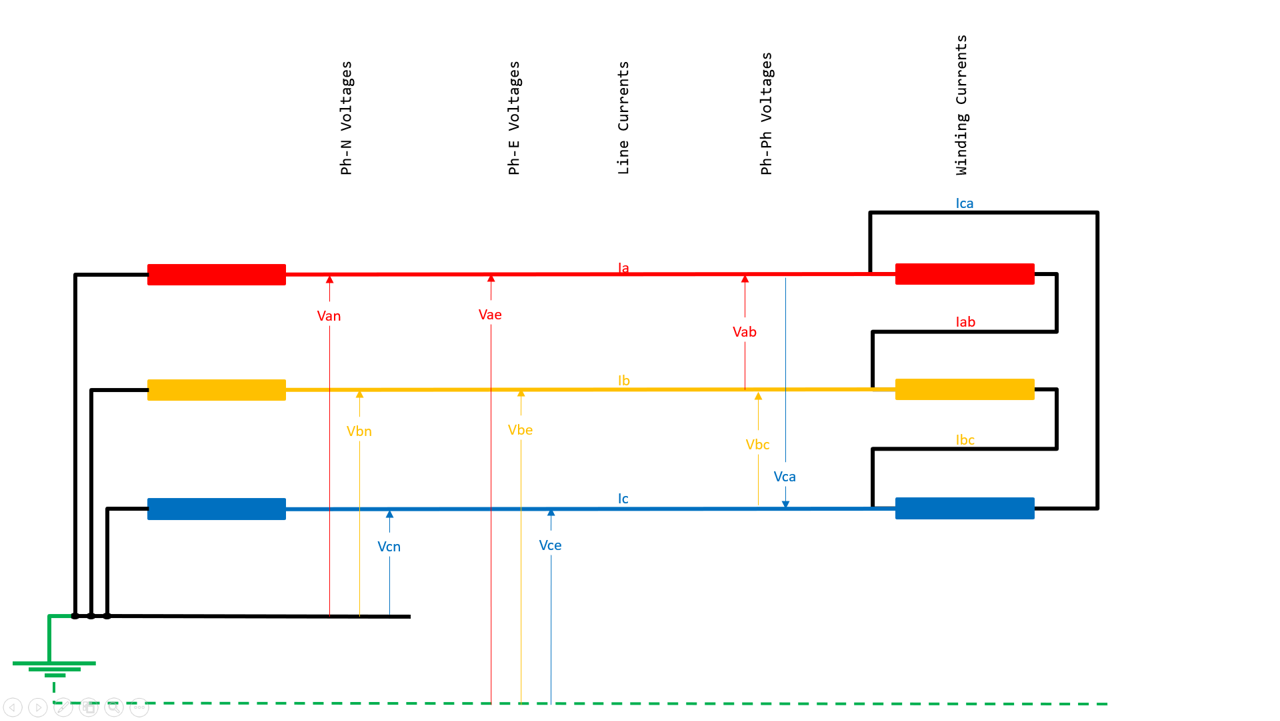 Image Removed Image Removed
Any set of three phase measurements of Magnitude AND Relative Phase Angle between the phasors can be analysed using the Sequence Component Formulas: - Positive Sequence A = ( A + αB + α²C ) / 3
- Negative Sequence A = ( A + α²B + αC ) / 3
- Zero Sequence A = ( A + B + C ) / 3
where the measured values are magnitude and relative phase angle values - A = A_magnitude @ A_angle (A_angle can often be stated as 0 as a "reference" phasor)
- B = B_magnitude @ B_angle (B_angle is with respect to the A phasor)
- C = C_magnitude @ C_angle (C_angle is with respect to the A phasor)
- α = 1 @ 120°
Note these relative phase angles are NOT the phase angle associated with Power Factor. Power Factor angle refers to the relationship between voltage and current which is distinctly different to the angle relationship between the three currents or angle relationship between the three voltages. These formulas allow us to derive nine Sequence Component Phasors Positive Sequence (generally designated as a suffix "1") A1 = A1_magnitude @ A1_angle B1 = B1_magnitude @ B1_angle C1 = C1_magnitude @ C1_angle where - A1_magnitude = B1_magnitude = C1_magnitude
- B1_angle = A1_angle - 120
- C1_angle = B1_angle - 120
Negative Sequence (generally designated as a suffix "2") A2 = A2_magnitude @ A2_angle B2 = B2_magnitude @ B2_angle C2 = C2_magnitude @ C2_angle where - A2_magnitude = B2_magnitude = C2_magnitude
- B2_angle = A2_angle - 120
- C2_angle = B2_angle - 120
Zero Sequence (generally designated as a suffix "0") A0 = A0_magnitude @ A0_angle B0 = B0_magnitude @ B0_angle C0 = C0_magnitude @ C0_angle where - A0_magnitude = B0_magnitude = C0_magnitude
- A2_angle = B2_angle = C2_angle (all in phase)
This spread sheet provides a tool for converting the 3-phase phasors into their Sequence Components. Click to download the spreadsheet: Sequence Components.xlsx Analysis examplesFor a balanced condition, all phases are equal magnitude and 120 degrees separation in the right sequence and would therefore be analysed as pure Positive Sequence, no Negative or Zero Sequence. This would remain true at any value of the balanced phasors and hence we must take care in setting protection functions not to operate for balanced loads from zero to rated values, and knowing that even large changes below rated values are not necessarily indicative of an actual fault. However if the phasors become unbalanced for any reason ,i.e. no longer equal magnitude and/or no longer 120 degrees separation, Negative Sequence and/or Zero sequence will be seen which will be a very clear indication of some kind of fault - they are normally zero but become non-zero. Hence some functions are assigned to operate on the basis of Negative Sequence detection changing from zero. Of course Zero Sequence detection has always been available as the earth fault element. Older electro-mechanical relays required complicated extra hardware filters to extract Negative Sequence component. The advent of numerical relays has provided easier detection of Sequence Components using algorithms. Sequence Components are mathematical analysis of a set of three phasors. They are not "real" world physical measurements. You cannot connect a multi-meter to any point and measure a Sequence Component! Even if you use a multi-meter to measure all three phases as the same magnitude, you also need to know they are exactly 120° apart to know that the values are balanced and therefore would be the Positive Sequence value with no Negative or Zero Sequence component. - The "closest" you get is if you know there is no current in two of the three phases but current in the third, you know the third current is 3 x the Zero Sequence.
- Or if you measure the current in the earth-neutral leg, that current is 3 x the Zero Sequence.
- Or the current in the delta itself is the actual Zero Sequence value IF all three windings are the same magnitude AND they must also be in-phase (consider a Dyn TF with balanced load .. the D winding currents are all the same magnitude but not in-phase).
Example 1: Balanced 3-phase is all positive sequence  Image Removed Image Removed
Example 2: general unbalance magnitudes and angles results in a full set of Sequence Components  Image Removed Image Removed
Example 3: a single phase condition would result in these components (e.g. the star side of a Dyn transformer with a single phase load or fault on the star, or the currents in the delta windings):  Image Removed Image Removed
Example 4: a phase-to-phase condition would result in these components: (e.g. the line connections to the delta side of a Dyn transformer with a single phase load or fault on the star)  Image Removed Image Removed
A common question when first dealing with Sequence Components is : How are Zero Sequence current eliminated in delta windings. First you have to remember that Sequence Components are not “real” – they are mathematical derivations from the real currents, but the sum of all Components add up to equal the real currents.
Hence for a set of 3 phase phasors, there are nine Sequence Component phasors: 3 x Positive Sequence, 3 x Negative Sequence and 3 x Zero Sequence. Second, real currents must obey Ohm’s Law and Kirchoff’s Law … they must have a path to flow.
So do Sequence Components, but the real paths have to be converted into equivalent Sequence Component paths and equivalent Sequence Component impedances, although that is not the focus of this information. YNynConsider a low voltage star winding of a transformer. Single phase current can flow if there is a connection to the star (neutral) point of the transformer … - 4‑wire systems of course mean single phase loads can have current in one phase flowing back via the neutral wire.
- 3-wire, or 4-wire systems with earthed neutral will allow single phase earth fault currents to flow in one phase flowing back via the earth.
So the real current distribution of a single phase condition (load or earth fault), the three phases would be termed “1-0-0”.
Refer Example #3 above.
With current in one phase, the Sequence Component Analysis shows that there is Positive, Negative and Zero Sequence current flowing in all three phases and they “flow” through the equivalent three phase Positive, Negative and Zero Sequence path impedance of each phase, even though the real impedance on the two phases with zero real current is effectively an open circuit.
The A, B and C zero sequence currents would all add up to be the value of the real current because as zero sequence they are all in phase.
i.e. I-single-phase = 3 x I-zero-sequence So now consider that single phase LV current in a star winding for a YNyn arrangement, i.e. neutral connections on both windings
On a star HV winding, that LV current must cause equal Ampere.Turns balance on the HV winding, i.e. real current in one LV winding needs to cause real current in one HV winding to maintain Ampere.Turns balance.
Being a star HV winding arrangement, there can only be current flowing in one HV winding corresponding to the LV winding with real current flow. There can be no current in the other two HV windings because there is no current in the other two LV windings.
That being the case, then the real HV currents would also be termed “1-0-0” distribution and would also be analysed with Positive, Negative and Zero Sequence components. DynIf the HV winding is delta, i.e. Dyn, Ampere.Turns must still balance LVwinding-to-HVwinding.
So one of the delta limb windings will have current flowing to balance its corresponding LV winding.
At each bushing there are three connections – two winding ends and the line.
Kirchoff’s Law is that the sum of the currents in and out of a node must equal zero.
We know that one winding has current flow, the other winding has none, so the current flow must be on the line connected to the node.
That happens because when you look at the currents in the windings (i.e. not the line currents), the winding currents are still “1-0-0” due to Ampere.Turns balance.
That HV winding current can only flow into the TF bushing from one phase connection and out on another phase connection at the other end of the winding, i.e. there is line current flowing "into" the bushing on A phase and out of the other bushing on B phase.
We would therefore term the line currents as a “1-1-0” where the two line currents are equal magnitude and opposite directions.
If you now do the Sequence Components of a “1-1-0” as in Example #4 above, you will see that there is only Positive and Negative Sequence … no Zero Sequence at all.
We therefore say that the Delta winding is a "Zero Sequence Trap".
The delta winding currents ar "1-0-0" distribution to achieve Ampere.Turns balance with the LV windings. That means that within the windings, there are Positive, Negative and Zero Sequence components.
Therefore the magnitude and phase angle of the A winding, B winding and C winding Zero Sequence currents are all exactly the same.
Therefore applying Kirchoff’s Law, if the current flowing into the node from one winding equals the current flowing out of the node into the other winding, there can be no Zero Sequence current flowing on the line as proven in the previous paragraph.
All the Zero Sequence currents happily flow around the HV Delta winding, but do not flow on the HV line phases.
Hence the Delta has "trapped" the zero sequence current.
(For the same reason, delta windings are also a 3rd harmonic trap as the 3rd harmonics are inherently in phase.)But note: a common misunderstanding is that Delta windings do not result in any zero sequence current .. ever!
If you have an earth fault on the HV delta winding,.., in the worst case say a bushing to earth, there will be current flowing down the one line to the faulted bushing. That would still be “1-0-0” so Zero Sequence still exists. Mid-winding faults would be more complicated with real currents flowing in all three lines, but will still analyse as having some Zero Sequence| Tip |
|---|
| title | Analysis spreadsheet to download |
|---|
| "Cutting to the chase" ... I have provided a spreadsheet tool below (as I have used in the examples on this page) for you to use as direct graphical and numerical display ... This spread sheet provides a tool for converting the 3-phase phasors into their Sequence Components. - Download
- Select Voltage or Current analysis
- Select manual or automatic per unit scale
- Enter your phasor values in the top-left field boxes

Click to download the spreadsheet: Sequence Components.xlsx
When the preview opens, select the download button top-right corner  Image Added Image Added Latest version Tuesday 01-August 2023 |
Kirchhoff's Law tells us that the sum of the currents at any node must equal zero.
Hence at a star point of three phases and a fourth connection to neutral, those four currents flowing in and out of the star POINT must sum to zero. Ia + Ib + Ic + In = 0 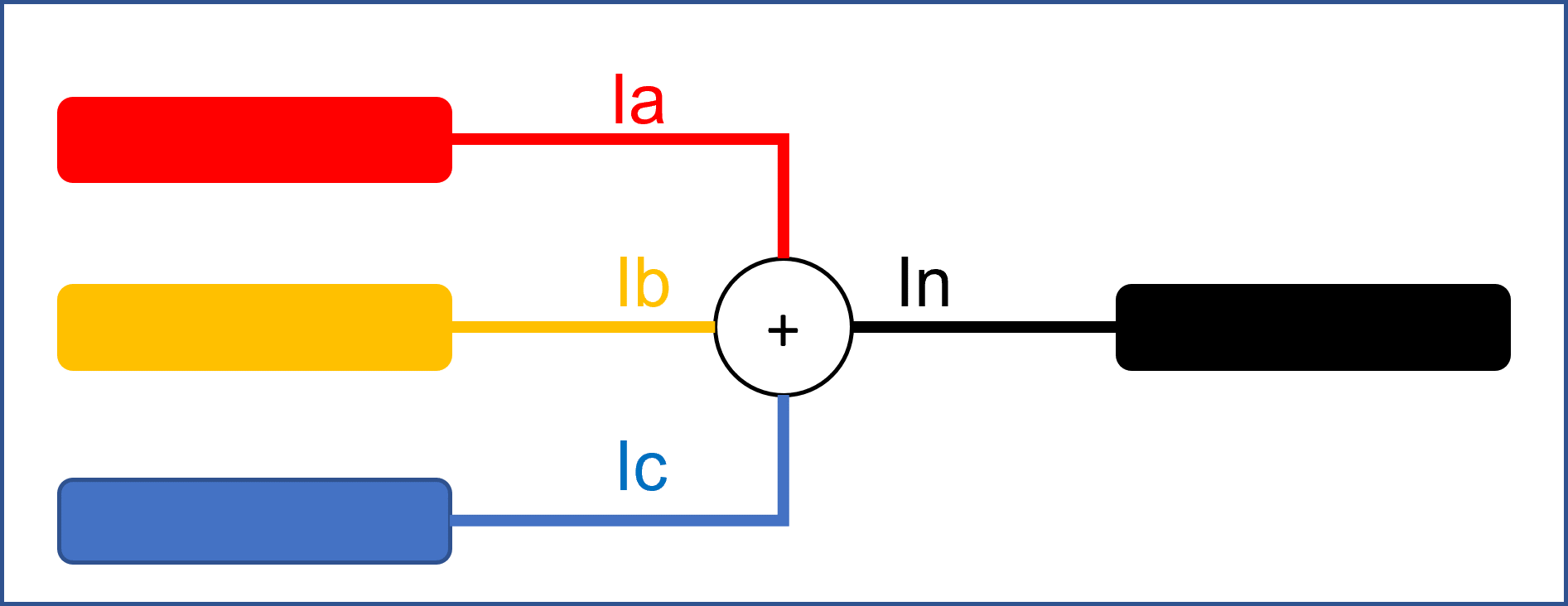 Image Added Image Added
But mathematically, what is "In"?
It could be - a 3-phase, 3 or 4 wire ungrounded system ... with or without a fault
- a 3-phase, 3 or 4 wire grounded system... with or without a fault
Therefore In itself could be a sum of the neutral wire and any earth current. In could relate to a source or a load. 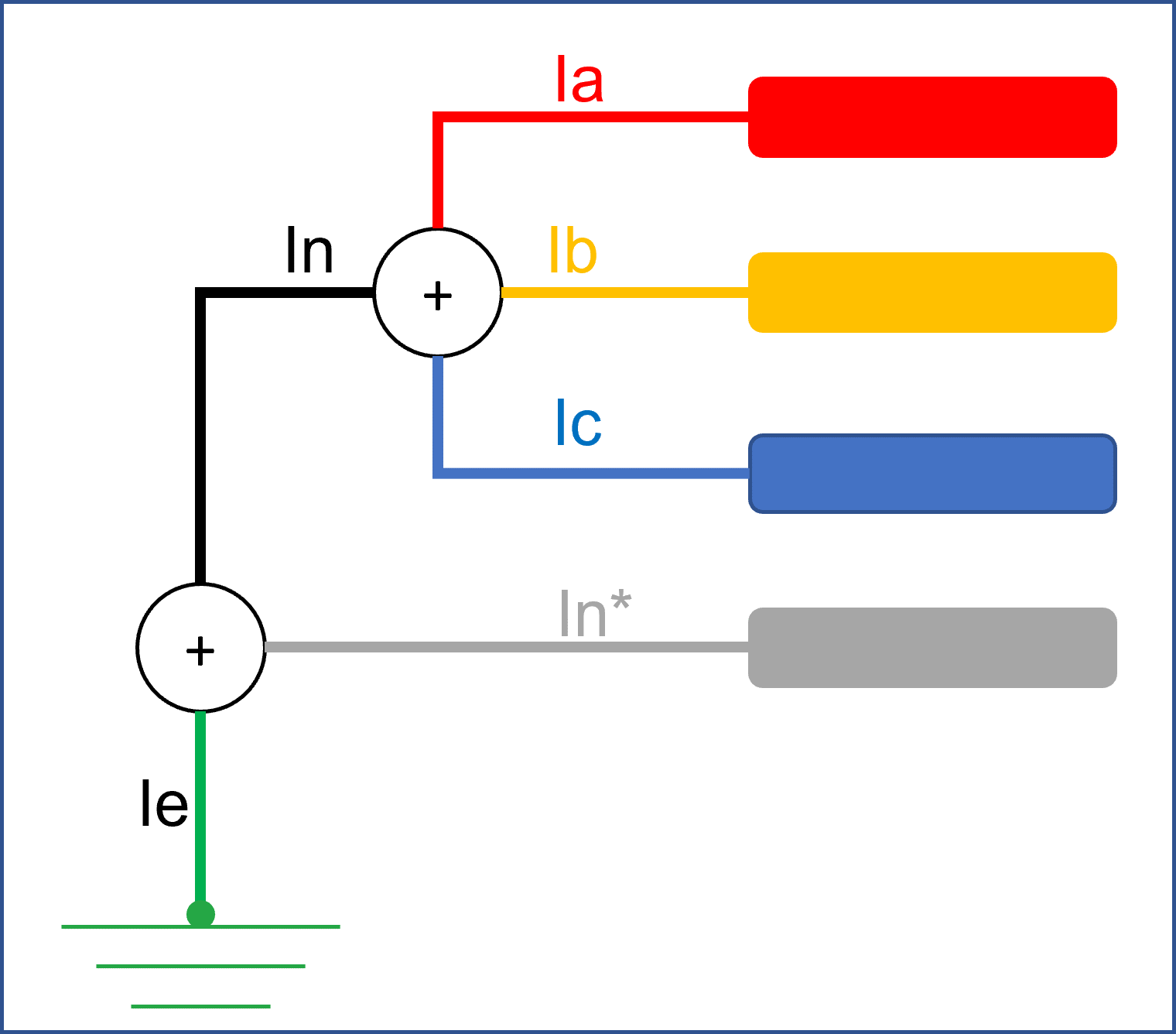 Image Added Image Added 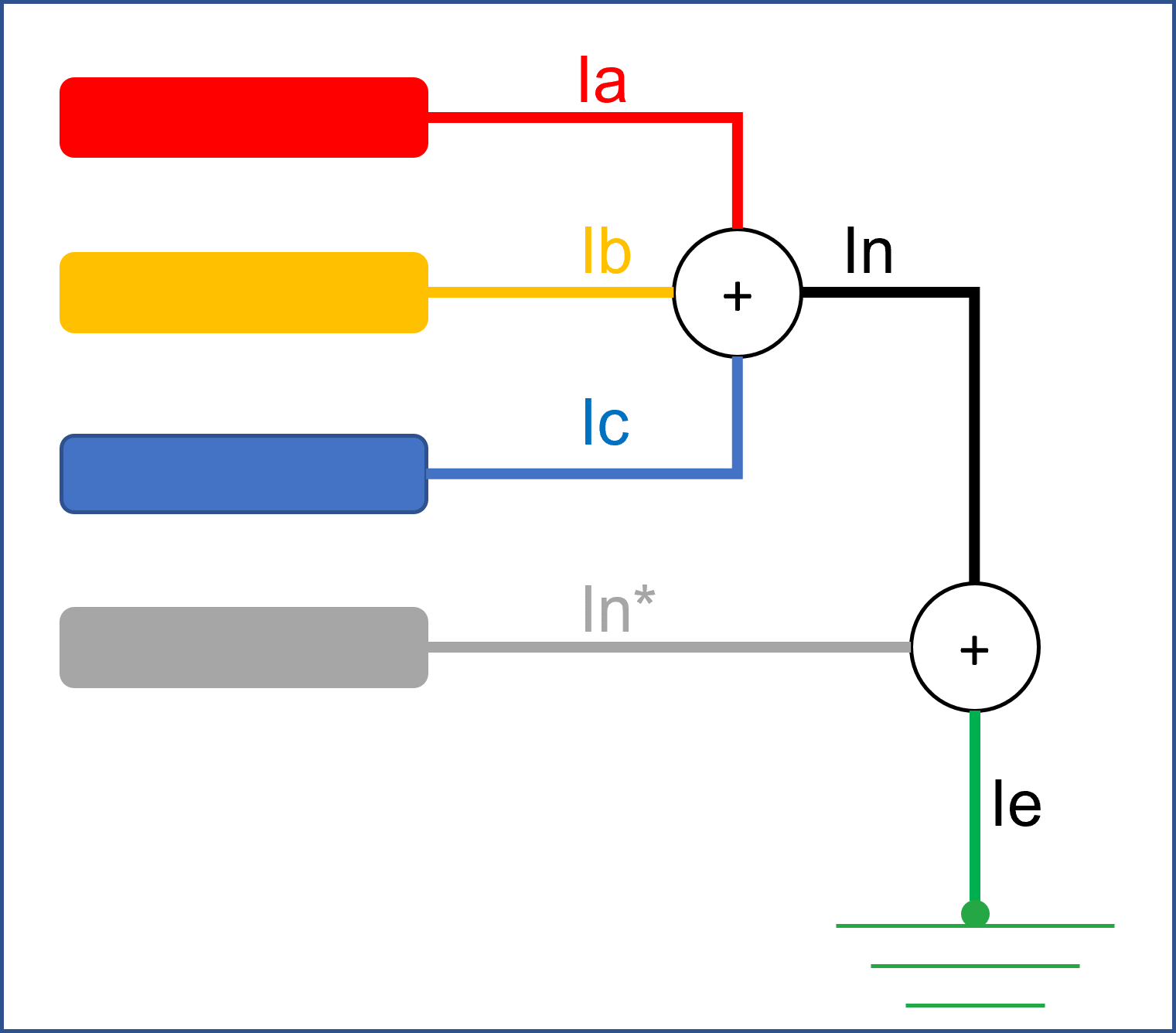 Image Added Image Added
Or it could be "anywhere in between" a source and the load with or without a neutral wire and with or without an earth. 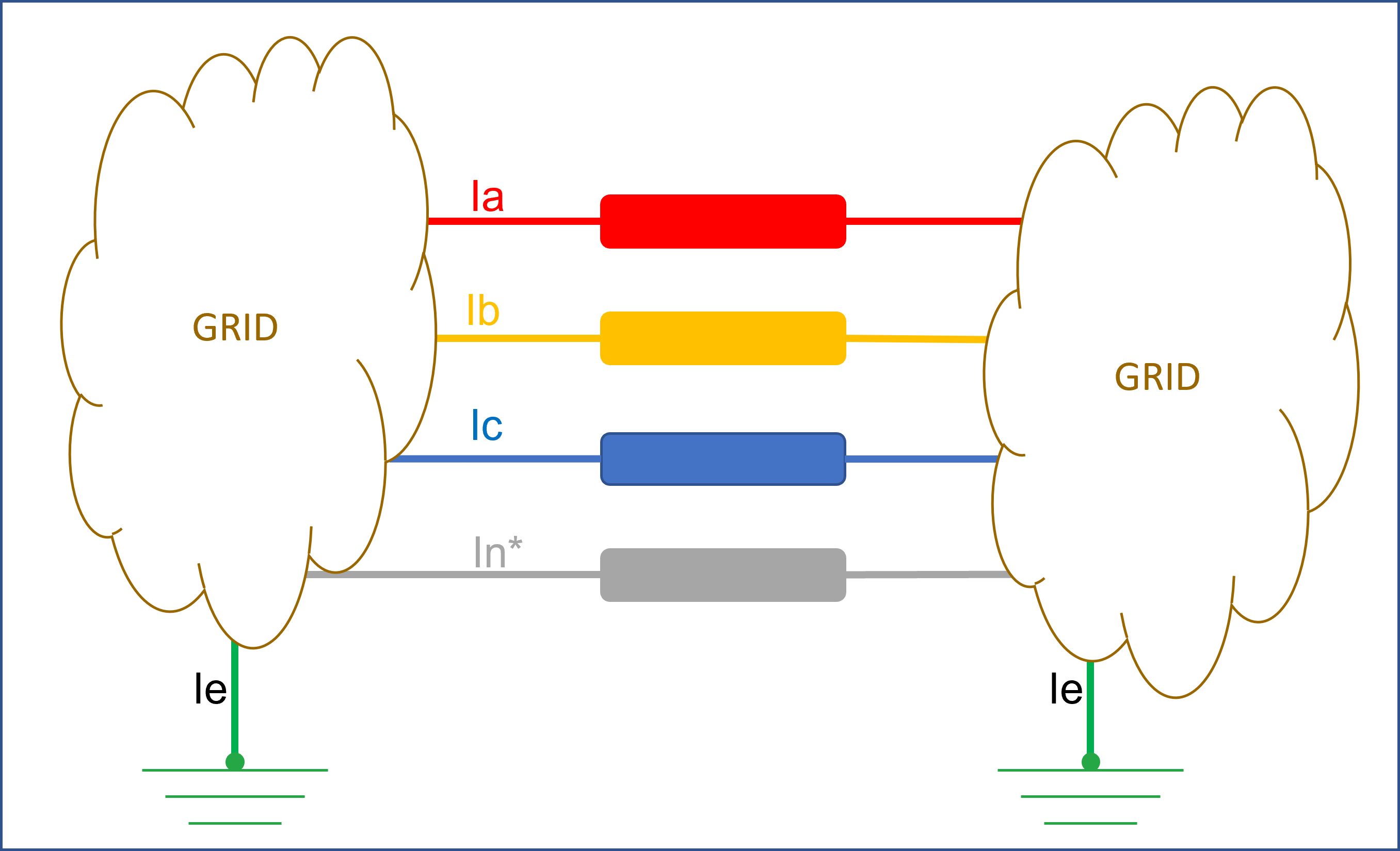 Image Added Image Added
But what if we only know the currents on the three lines: Ia, Ib, Ic.
They do not necessarily add to zero because Ia + Ib + Ic = -In In some cases the three phasors may represent a perfectly normal system condition such as: - a single phase load on the star side of a delta-star transformer where the three individual phase currents Ia, Ib, Ic which clearly do not sum to zero,
- whereas the associated phase-to-phase current seen on the delta side where the three individual phase currents do sum to zero.
System Components is a mathematical treatment of the magnitudes and phase angles of the three individual phase measurements that allows us to know far more about the nature of the power system condition than just the measurements alone. Sequence Components are mathematical analysis of a set of three phasors. They are not "real" world physical measurements. You cannot connect a multi-meter to any point and measure a Sequence Component! The objective is to analyse and understand the real system measurements to tell us something more useful than just the magnitudes and angles alone.
Is this a normal condition or is it a bad condition? The Symmetrical Component formulas can be applied to the measurements of the three 3-phase currents, ... or the measurements of three 3-phase voltages. The combined results of the Symmetrical Components formulas can HELP us discover more about the nature of the power system and hence HELP us decide what to do about it. | Tip |
|---|
| We can set a "pure" magnitude based threshold of the measurements as an indicator of a fault ... an overcurrent setting, or an undervoltage setting or a under/over power ..... But what if there is a "non-healthy" condition where the magnitude of the measurement is still not a trigger for the under or over the threshold? The Symmetrical Component values may show us that what we would consider "should be a zero value" Component is now a non-zero value ... and the magnitude of that non-zero value may be an indicator of how severe the condition may be. It may be any set of three currents or three voltages. |
| Info |
|---|
| title | Myths and Misunderstandings |
|---|
| Sequence Components does not state that the real system 3-phase currents sum to zero, or that real system 3-phase voltages sum to zero. In fact the Symmetrical Component formulas are because the system sometimes does NOT sum to zero across the three phases,
... or they DO sum to zero, but the phases are not equally balanced on all three phases! We are not talking about d.c. offsets, inrush transients or decaying/decrement waveforms which may affect one or more phases differently to the other for a few, or indeed many cycles. We are not talking about the “super-fast” so-called travelling wave disturbances when a fault occurs. We are not talking about waveforms with harmonics. We are talking about the normal system fundamental frequency r.m.s. currents or voltages that you can measure with a "voltmeter" or "ammeter" and a "phase angle meter"! |
The sum of the three phase currents at the star point of an electrical power system would be zero if the power system was perfectly balanced: i.e. IF the electrical power system was all “perfect” with equal voltage magnitude and 120 degrees angle between and with them equal impedances and loads on each phase. But that is often not the case for faulted conditions .... or even essentially "healthy" conditions: - Voltages may be slightly different magnitude
- Angles between the voltages phasors may not be exactly 120 degrees
- The conductor impedances may not be exactly the same per phase
- The loads may be different per phase
- There may be single phase loads
- There may be two-phase loads connected between just two phases
- There may be a single phase fault to earth/ground
- There may be a phase-to-phase fault
- There may be a fault across all three phases
- There may be a phase-to-earth fault on the secondary star winding of a delta-star transformer, seen as a phase-to-phase fault on the delta side.
- There may be a phase-to-phase fault on the secondary star winding of a delta-star transformer, seen as a "1-2-1" fault on the delta side
So the system at any point may have slightly ... or severely ... “Unbalanced” measurements of the three phase voltage and/or current. Such conditions can be seen in these examples .. some are "subtle" minor variations between the magnitudes and/or phase angles, .... some extreme. A phase current is 200 A @ 0°
B phase current is 220 A @ -115°
C phase current is 180 A @ -235°
Star point Neutral current is 52.08 A @ -85.9° 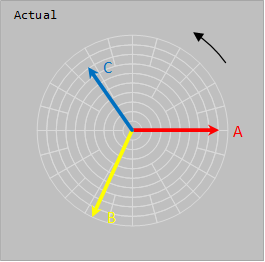 Image Added Image Added 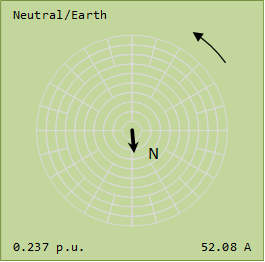 Image Added Image Added
A phase current is 0 A
B phase current is 1500 A @ -115°
C phase current is 0
Star point Neutral current is 1500 A @ -115°  Image Added Image Added 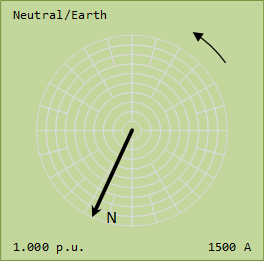 Image Added Image Added
A phase current is 200 A @ 0°
B phase current is 0 A
C phase current is 180 A @ -235°
Star point Neutral current is 176.3 A @ -56.7° 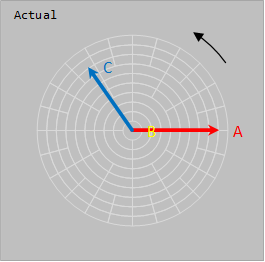 Image Added Image Added 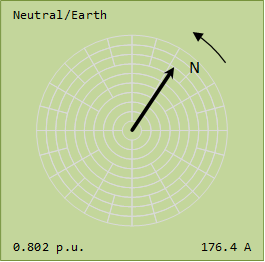 Image Added Image Added
A phase current is 0 A
B phase current is 200 A @ -115°
C phase current is 200 A @ -295°
Star point Neutral current is 0 A Note the three phase currents all sum to zero, but the three phases are definitely not balanced! 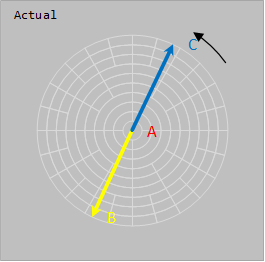 Image Added Image Added  Image Added Image Added
This unbalance may be useful for fault detection, but equally may be a normal power system condition.
Hence the "nature" of the unbalance needs some analysis tool. Many decades ago, the mathematical formulas were developed which we know as Symmetrical Components.
Symmetrical Components can provide some more detail about the nature of the measured values that leads to more precise fault detection decisions, as well as determination of the impact of the unbalance on the primary generator, transformer and motor equipment. | Info |
|---|
| title | Symmetrical Components |
|---|
| Symmetrical Components says that if there are “n” phases across 360 degrees, there are precisely three equations that define 3 sets of n phasors i..e - “n” Positive Sequence phasors, each 360/n degrees apart of equal magnitude
- “n” Negative Sequence phasors, each 360/n degrees apart of equal magnitude
- “n” Zero Sequence phasors, each 360/n degrees apart of equal magnitude
Therefore the three (voltage or current) phasor values of a 3-phase power system can be analysed into a total of nine (voltage or current) symmetrical component phasors. | Positive Sequence A phase | Positive Sequence B phase | Positive Sequence C phase | | Negative Sequence A phase | Negative Sequence B phase | Negative Sequence C phase | | Zero Sequence A phase | Zero Sequence B phase | Zero Sequence C phase |
|
| Tip |
|---|
Note that just connecting a standard ammeter to one phase of the power system will not be able to measure any of the Sequence Components. The closest to a direct ammeter measurement is the neutral star point connection where that current equals three times any one of the Zero Sequence Components i.e.
Zero Sequence Current = 1/3 of the Neutral Current |
The history of who and why they were developed is interesting, but these days is relatively unimportant if you just want to use the formulas to help your analysis.
They simply exist. Positive, Negative and Zero Sequence Components are often a key aspect of analysis of power system conditions. They can be used to analyse any of the five sets of 3-phase Phasors as shown in the following diagram:  Image Added Image Added
Any set of three phase measurements of Magnitude AND Relative Phase Angle between the phasors can be analysed using the Sequence Component Formulas. Consider three phase measurements as: - A = A_magnitude @ A_angle (A_angle is with respect to the reference angle, but is often set as the reference phasor at 0°)
- B = B_magnitude @ B_angle (B_angle is with respect to the reference angle)
- C = C_magnitude @ C_angle (C_angle is with respect to the reference angle)
where the measured values are magnitude and relative phase angle values compared to the reference 0° angle. Note these relative phase angles are NOT the phase angle associated with Power Factor.
Power Factor angle refers to the relationship between voltage and current which is distinctly different to the angle relationship between the three currents or angle relationship between the three voltages.
The angle here is between three current phasors, or the angle between three voltage phasors. There is a mathematical "operator" with the Greek symbol alpha:
α = 1 @ 120°
Multiplying a phasor by α effectively rotates the phasor by 120°, α² rotates by 240°. These formulas allow us to derive nine Sequence Component Phasors. Considering measurements for A, B and C phases, we can derive the three Sequence Components of the A phase as follows. | A1 | = | ( A + αB + α²C ) / 3 | | A2 | = | ( A + α²B + αC ) / 3 | | A3 | = | ( A + B + C ) / 3 |
Similar formulas apply for the B and C phases, i.e. for a 3-phase set of measured phasors, there are 9 individual sequence component phasors. Positive Sequence (generally designated as a suffix "1") By definition, the three phase values of positive sequence are the same magnitude and precisely 120° apart and rotate in the forward sequence ABCABCABC A1 = A1_magnitude @ A1_angle
B1 = B1_magnitude @ B1_angle
C1 = C1_magnitude @ C1_angle where - A1_magnitude = B1_magnitude = C1_magnitude
- B1_angle = A1_angle - 120°
- C1_angle = B1_angle - 120° = A1_angle - 240°
Negative Sequence (generally designated as a suffix "2") By definition, the three phase values of negative sequence are the same magnitude and precisely 120° apart, BUT they rotate in the reverse sequence CBACBACBA A2 = A2_magnitude @ A2_angle
B2 = B2_magnitude @ B2_angle
C2 = C2_magnitude @ C2_angle where - A2_magnitude = B2_magnitude = C2_magnitude
- B2_angle = A2_angle - 120°
- C2_angle = B2_angle - 120°
Zero Sequence (generally designated as a suffix "0") By definition, the three phase values of zero sequence are the same magnitude and precisely in-phase, and rotate together. A0 = A0_magnitude @ A0_angle
B0 = B0_magnitude @ B0_angle
C0 = C0_magnitude @ C0_angle where - A0_magnitude = B0_magnitude = C0_magnitude
- A2_angle = B2_angle = C2_angle (all in phase)
The Symmetrical Component formulas are well known for many decades.
Just about any power systems analysis or protection book will provide the details of the formulas.
You just need to use the three measurements of magnitude and angle of each of the 3-phase Phasors. Many system monitoring (SCADA), test tools and test equipment will do the analysis and display/use the results for you. Of course you can create a spreadsheet or some sort of tool or "app" that will do the maths for you. | Tip |
|---|
| title | Analysis spreadsheet to download |
|---|
| I have provided a spreadsheet tool below for you to use in direct graphical and numerical display ... This spread sheet provides a tool for converting the 3-phase phasors into their Sequence Components. - Download
- Select Voltage or Current analysis
- Select manual or automatic per unit scale
- Enter your phasor values in the top-left field boxes

Click to download the spreadsheet: Sequence Components.xlsx |
For a balanced condition, all phases are equal magnitude and 120 degrees separation in the right sequence and would therefore be analysed as pure Positive Sequence, no Negative or Zero Sequence. This would remain true at any value of the balanced phasors and hence we must take care in setting protection functions not to operate for balanced loads from zero to rated values, and knowing that even large changes below rated values are not necessarily indicative of an actual fault. However if the phasors become unbalanced for any reason ,i.e. no longer equal magnitude and/or no longer 120 degrees separation, Negative Sequence and/or Zero sequence will be seen which will be a very clear indication of some kind of fault - they are normally zero but become non-zero. Hence some functions are assigned to operate on the basis of Negative Sequence detection changing from zero. Of course Zero Sequence detection has always been available as the earth fault element. Older electro-mechanical relays required complicated extra hardware filters to extract Negative Sequence component. The advent of numerical relays has provided easier detection of Sequence Components using algorithms. Even if you use a multi-meter to measure all three phases as the same magnitude, you also need to know they are exactly 120° apart to know that the values are balanced and therefore would be the Positive Sequence value with no Negative or Zero Sequence component. - The "closest" you get is if you know there is no current in two of the three phases but current in the third, you know the third current is 3 x the Zero Sequence.
- Or if you measure the current in the earth-neutral leg, that current is 3 x the Zero Sequence.
- Or the current in the delta itself is the actual Zero Sequence value IF all three windings are the same magnitude AND they must also be in-phase (consider a Dyn TF with balanced load .. the D winding currents are all the same magnitude but not in-phase).
This is all positive sequence 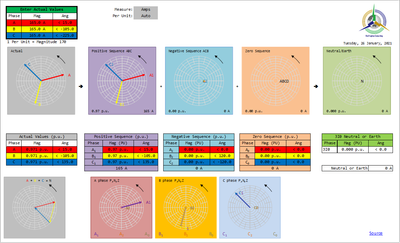 Image Added Image Added
This results in a full set of Sequence Components 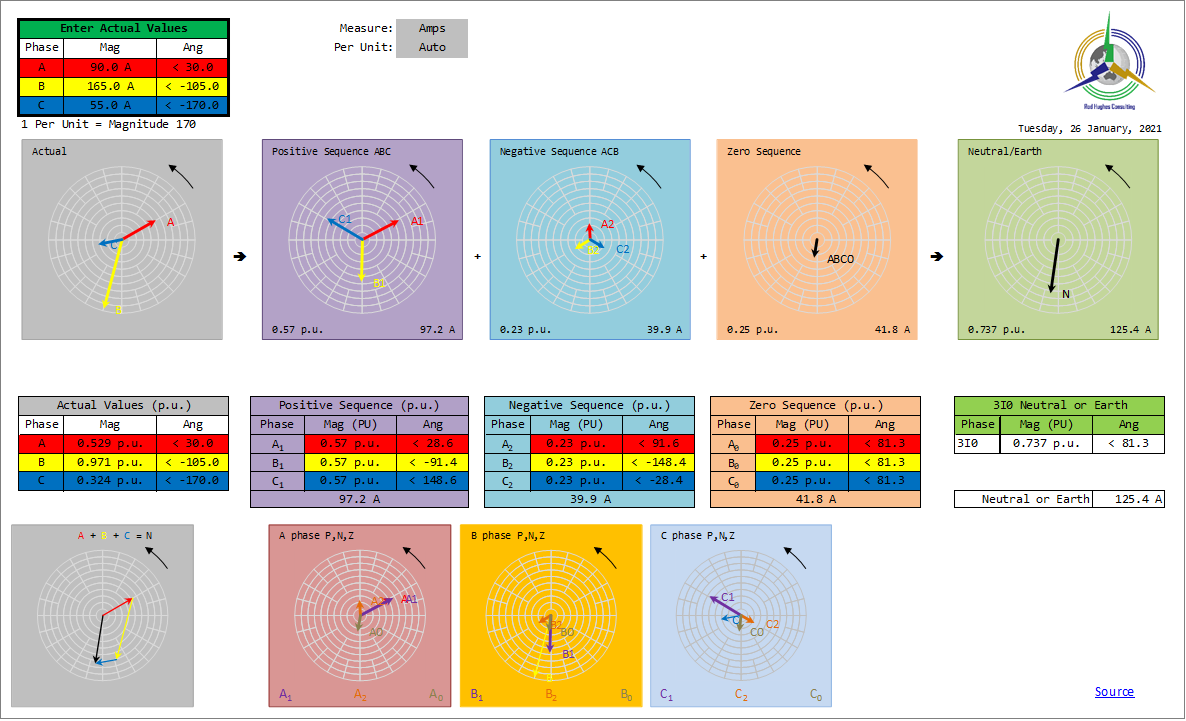 Image Added Image Added
This would result in these components (e.g. the star side of a Dyn transformer with a single phase load or fault on the star, or the currents in the delta windings): 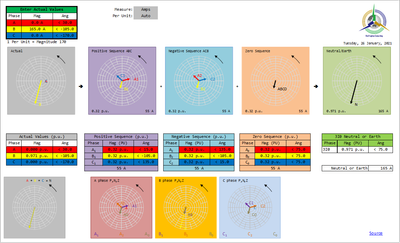 Image Added Image Added
This would result in these components: (e.g. the line connections to the delta side of a Dyn transformer with a single phase load or fault on the star) 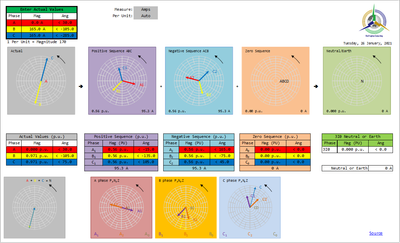 Image Added Image Added
e.g. assuming the phase-to-neutral voltages are all balanced at 120 degrees apart and A phase voltage is reference 0°: A_phase 0.95 lagging (-18°) means the A phase current phasor is at -18° with respect to the A phase voltage, B_phase 0 PF, means the B phase current is in phase with the B phase voltage, i.e. at -120° with respect to the A phase voltage, C_phase 0,85 leading (+31°) means the C phase current is leading the C phase voltage by 31°, i.e. -209° with respect to the A phase voltage 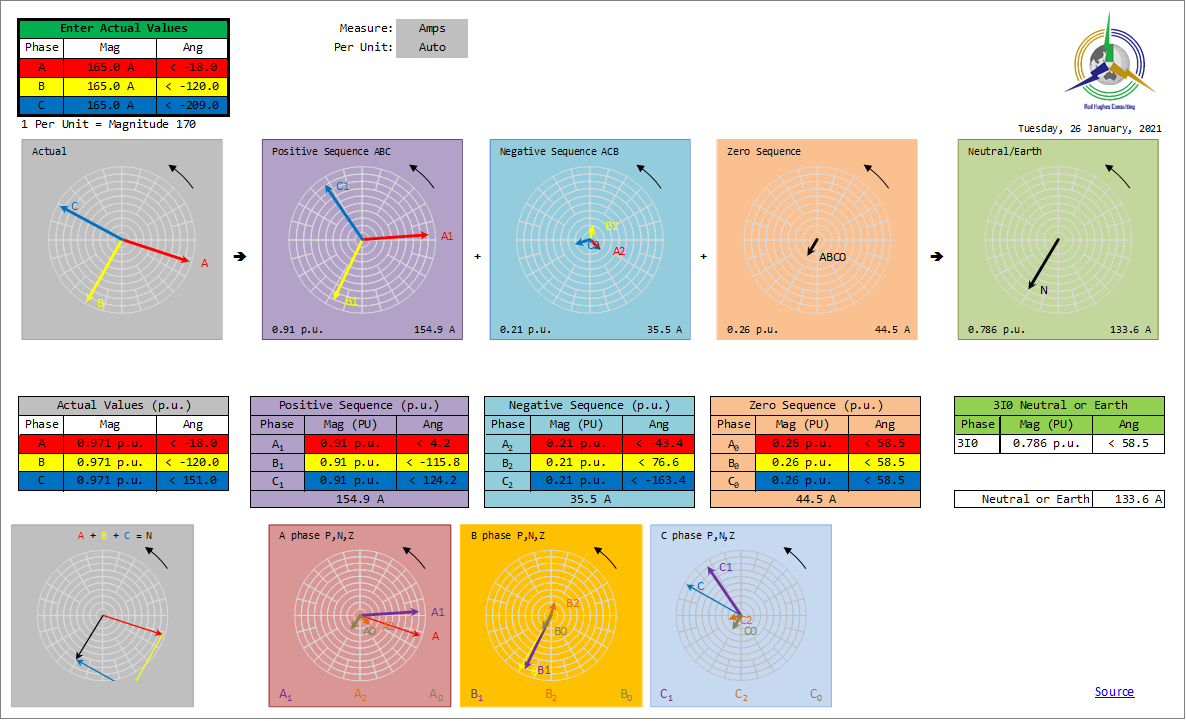 Image Added Image Added
If the voltages are also unbalanced, we can derive the voltage Sequence Component values, form which we can derive a "Sequence Component Power Factor from the Sequence Component Currents. 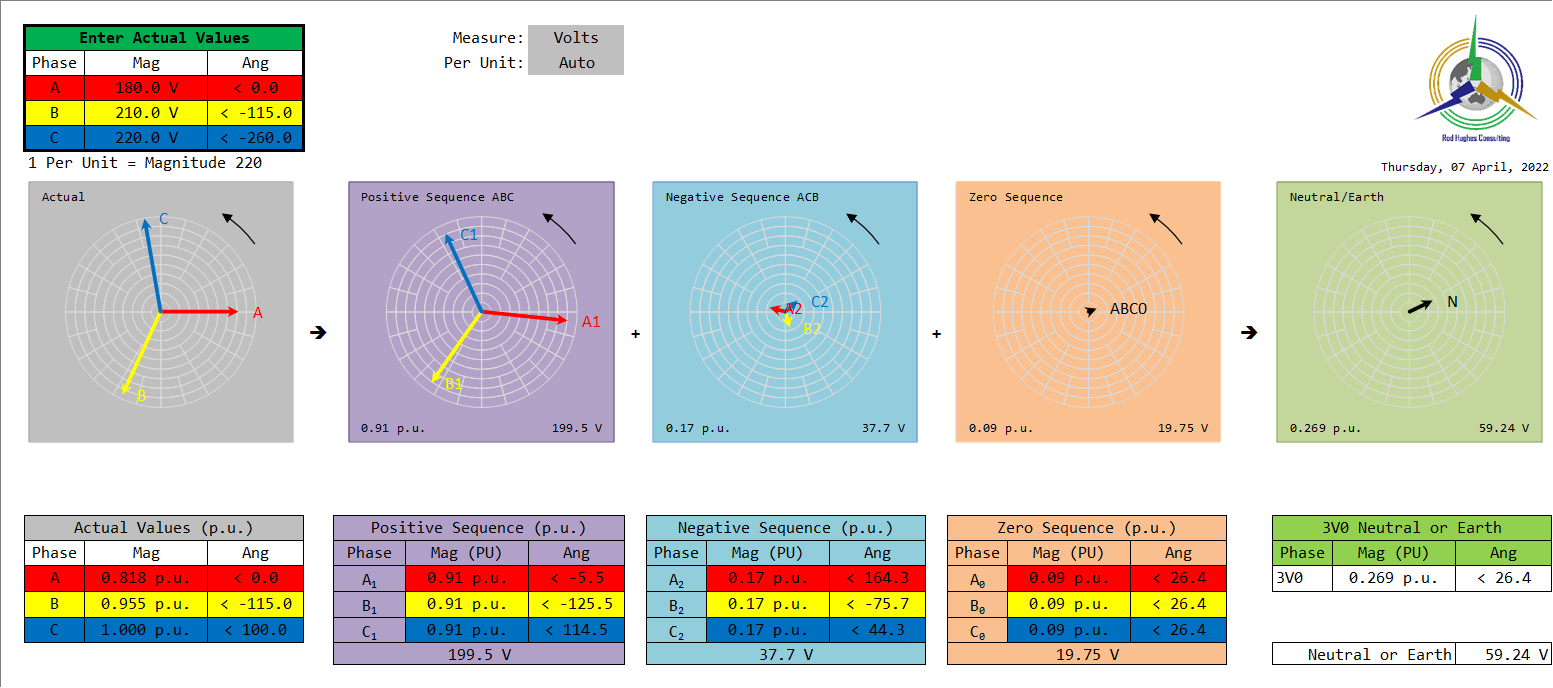 Image Added Image Added
Hence for A phase, B phase and C phase we have the same "balanced power factors" based on the phase angles of the currents to their respective voltages | Value | Positive Sequence | Negative Sequence | Zero Sequence |
|---|
| Voltage | 199.5 V @ -5.5° | 37.7 V @ +164.3° | 19.75 V @ +26.4° | | Current | 154.9 A @ +4.2° | 35.5 A @ -43.4° | 44.5 A @ +58.5° | Phase Angle | 4.2 - (-5.5) +9.7° | -43.4 - (164.3) -207.7° = +152.3° | 58.5 - (26.4) +32.1° | | PF | 0.986 Leading | 0.885 Leading | 0.847 Leading |
A common question when first dealing with Sequence Components is : How are Zero Sequence current eliminated in delta windings. First you have to remember that Sequence Components are not “real” – they are mathematical derivations from the real currents, but the sum of all Components add up to equal the real currents.
Hence for a set of 3 phase phasors, there are nine Sequence Component phasors: 3 x Positive Sequence, 3 x Negative Sequence and 3 x Zero Sequence. Second, real currents must obey Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff's Law … they must have a path to flow.
So do Sequence Components, but the real paths have to be converted into equivalent Sequence Component paths and equivalent Sequence Component impedances, although that is not the focus of this information. Consider a low voltage star winding of a transformer. Single phase current can flow if there is a connection to the star (neutral) point of the transformer … - 4‑wire systems of course mean single phase loads can have current in one phase flowing back via the neutral wire.
- 3-wire, or 4-wire systems with earthed neutral will allow single phase earth fault currents to flow in one phase flowing back via the earth.
So the real current distribution of a single phase condition (load or earth fault), the three phases would be termed “1-0-0”.
Refer Example #3 above.
With current in one phase, the Sequence Component Analysis shows that there is Positive, Negative and Zero Sequence current flowing in all three phases and they “flow” through the equivalent three phase Positive, Negative and Zero Sequence path impedance of each phase, even though the real impedance on the two phases with zero real current is effectively an open circuit.
The A, B and C zero sequence currents would all add up to be the value of the real current because as zero sequence they are all in phase.
i.e. I-single-phase = 3 x I-zero-sequence So now consider that single phase LV current in a star winding for a YNyn arrangement, i.e. neutral connections on both windings
On a star HV winding, that LV current must cause equal Ampere.Turns balance on the HV winding, i.e. real current in one LV winding needs to cause real current in one HV winding to maintain Ampere.Turns balance.
Being a star HV winding arrangement, there can only be current flowing in one HV winding corresponding to the LV winding with real current flow. There can be no current in the other two HV windings because there is no current in the other two LV windings.
That being the case, then the real HV currents would also be termed “1-0-0” distribution and would also be analysed with Positive, Negative and Zero Sequence components. If the HV winding is delta, i.e. Dyn, Ampere.Turns must still balance LVwinding-to-HVwinding.
So one of the delta limb windings will have current flowing to balance its corresponding LV winding.
At each bushing there are three connections – two winding ends and the line.
Kirchoff’s Law is that the sum of the currents in and out of a node must equal zero.
We know that one winding has current flow, the other winding has none, so the current flow must be on the line connected to the node.
That happens because when you look at the currents in the windings (i.e. not the line currents), the winding currents are still “1-0-0” due to Ampere.Turns balance.
That HV winding current can only flow into the TF bushing from one phase connection and out on another phase connection at the other end of the winding, i.e. there is line current flowing "into" the bushing on A phase and out of the other bushing on B phase.
We would therefore term the line currents as a “1-1-0” where the two line currents are equal magnitude and opposite directions.
If you now do the Sequence Components of a “1-1-0” as in Example #4 above, you will see that there is only Positive and Negative Sequence … no Zero Sequence at all.
We therefore say that the Delta winding is a "Zero Sequence Trap".
The delta winding currents ar "1-0-0" distribution to achieve Ampere.Turns balance with the LV windings. That means that within the windings, there are Positive, Negative and Zero Sequence components.
Therefore the magnitude and phase angle of the A winding, B winding and C winding Zero Sequence currents are all exactly the same.
Therefore applying Kirchhoff's Law, if the current flowing into the node from one winding equals the current flowing out of the node into the other winding, there can be no Zero Sequence current flowing on the line as proven in the previous paragraph.
All the Zero Sequence currents happily flow around the HV Delta winding, but do not flow on the HV line phases.
Hence the Delta has "trapped" the zero sequence current.
(For the same reason, delta windings are also a 3rd harmonic trap as the 3rd harmonics are inherently in phase.) But note: a common misunderstanding is that Delta windings do not result in any zero sequence current .. ever!
If you have an earth fault on the HV delta winding,.., in the worst case say a bushing to earth, there will be current flowing down the one line to the faulted bushing. That would still be “1-0-0” so Zero Sequence still exists. Mid-winding faults would be more complicated with real currents flowing in all three lines, but will still analyse as having some Zero Sequence. As shown above, a heathy balanced 3-phase system should only show 100% Positive Sequence. If there is a single phase load it will have as equal Positive, Negative and Zero sequence magnitudes. If there is a phase-to-phase load it will show equal Positive and Negative sequence, no Zero sequence. As shown above, variations in the source, line impedance or the load impedances, even faults can lead to Negative and/or Zero Sequence. But can a nominally healthy operating system have pure Negative Sequence?
In general we would say "no" simply because the system is operating in an ABC rotation, hence there must be "some" Positive Sequence. However, it can happen .... First experience. A MAJOR popular TV prime time show was having its first broadcast from their new studio stage.
Lights, Camera, Action ... a few seconds later ... trip on reverse power. Next day I was ordered by the (somewhat "annoyed" ... 😡) TV HOST HIMSELF .. to test the relay several times both at site and back in my office ..
Perfect relay! But each time we connected in the system, the (induction disc) reverse power relay started to spin! After a very quick site investigation, the reason was found to be that the electrical contractors had assumed the street supply was ABC on the cross arm of the pole at the site gate where the connection was made. But I could see 200 m down the road there was the "usual" phase transposition to balance line losses and coupling.
That meant the street connection on the cross arm was ACB “rotation”. So in connecting the power relay with supposedly Ia and Vbc, it was actually Ia and Vcb … the voltage was 180° opposite, which meant the relay saw normal balanced healthy power flow as "nicely" sitting right in the operate zone. If they had used a Phase Sequence meter (a little 3-phase instrument with a spinning dial) they would have seen the negative phase sequence causing reverse spin They said they were wondering why ALL their new 3-phase air conditioners were spinning the wrong direction – they had assumed badly manufactured! 🤦♂️ Second experience A 30-year old generator was sent away for a refurbishment rewinding.
Connected up.
Closed CB with a normal "3-light synchronism" indicators.
BANG and LOTS of smoke. The 30-year old switchboard was assumed to be ABC because that is what the labels on the switchgear said the connections were … But again street supply was ACB. But during the factory refurbishment, they hadn't noticed the generator had been rewired on site 30 years ago with two phases swapped inside the terminal box to match the switchgear's actual electrical phase sequence.
Naturally they just rewired the generator to original manufacturer's design drawings.
Hence when it got back to site, it was connected but was effectively opposite phase sequence to the actual voltages in the switchboard.
Run up the generator, close the CB with counter phase sequences causing HUGE out of synchronism power flows COMPLETELY destroying the refurbished generator! 🤦♂️
Several months to get a NEW one delivered. They later found a site drawing in the (literally) bottom drawer from 30-years earlier with feint pencil marks stating the re-wiring INSIDE the generator terminal box when they were doing the original switchboard and generator installation. |